- Conditions
- Procedures
Hip Arthroscopy

Hip arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is a procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into your hip joint to check for any damage and repair it simultaneously. An arthroscope is a small, fiber-optic instrument consisting of a lens, light source, and video camera. The camera projects images of the inside of the joint onto a large monitor, allowing your surgeon to look for any damage, assess the type of injury and repair the problem.
Hip Labral Repair

Labrum is a ring of strong fibrocartilaginous tissue lining around the socket of the hip joint. Labrum serves many functions where it acts as a shock absorber, lubricates the joint, and distributes the pressure equally. It holds the head of the femur in place and prevents the lateral and vertical movement of the femur head within the joint. It also deepens the acetabular cavity and offers stability against femoral head translation.
Hip Cartilage Repair

Hip cartilage is a white, tough, flexible tissue covering the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) of your hip joint. It acts as a cushion or shock-absorber and allows the bones to slide over one another by providing a smooth surface in the joint.
Proximal Hamstring Repair

Hamstring injuries primarily occur when the muscle is exposed to extreme strain; when it is stretched beyond its ability or when it must withstand a sudden load. This is commonly seen while sprinting – the hamstring muscles must bear the body’s entire weight and experience extreme contraction as you push off the ground to move forward.
Hip Reconstruction

Hip reconstruction is a surgery to repair or replace a damaged hip joint that causes pain and limits your movement.
Hip Cartilage Restoration

Hip cartilage restoration is a surgical technique to repair damaged articular cartilage in the hip joint by stimulating new growth of cartilage or by transplanting cartilage into areas with defects in order to relieve pain and restore normal function to the hip. Articular cartilage damage can occur from normal wear and tear of the hip joints, increasing age, injury, or other disease conditions. When cartilage is damaged, it can cause severe pain, inflammation, stiffness, and decreased range of motion of the hip.
Trochanteric Bursa Injections
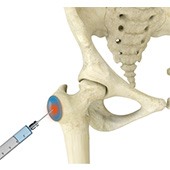
A trochanteric bursa injection is a minimally invasive procedure in which medicine is injected directly into the trochanteric bursa in the hip joint using a thin needle and syringe to relieve pain and inflammation. The injection usually contains a combination of numbing medicine and cortisone (an anti-inflammatory agent). Trochanteric bursitis, also known as greater trochanteric bursitis or hip bursitis, is the main indication for a trochanteric bursa injection.








